It all started in March 1992 when the first audiocast on the Internet took place from the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) meeting in San Diego. At that event 20 sites listened to the audiocast. Two years later, at the IETF meeting in Seattle about 567 hosts in 15 countries tuned in to the two parallel broadcasting channels (audio and video) and also talked back (audio) and joined the discussions! The networking community now takes it for granted that the IETF meetings will be distributed via MBone. MBone has also been used to distribute experimental data from a robot at the bottom of the Sea of Cortez (as will be described later) as well as a late Saturday night feature movie WAX or the Discovery of Television Among the Bees by David Blair.
As soon as some crucial tools existed, the usage just exploded. Many people started using MBone for conferences, weather maps, research experiments, to follow the Space Shuttle, for example. At the Swedish Institute of Computer Science (SICS) we saw our contribution to the Swedish University Network SUNET, increase from 26GB per month in February 1993 to 69GB per month in March 1993. This was mainly due to multicast traffic as SICS at that time was the major connection point between the U.S. and Europe in MBone.
MBone has also (in)directly been the cause of severe problems
in the NSFnet backbone, saturation of major international links rendering
them useless as well as sites being completely disconnected due to Internet
Connection Management Protocol (ICMP) responses flooding the networks.
We will expand on this later in this article.
First let us define what is meant by the different types ot "casting." The usual way packets are sent on the Internet is unicasting, that is, one host is sending to another specific single host. Broadcasting is when one host sends to all hosts on the same subnet. Normally, the routers between one subnet and another subnet will not let broadcast packets pass through. Multicasting is when one host sends to a group of hosts.
On the link level (e.g., Ethernet) multicasting has been defined for some time. On the network level (Interface Protocol or IP) it started with the work of Steve Deering of Xerox PARC when he developed multicast at the IP level [3]. The IP address space is divided into different classes. An IP address is four bytes and the address classes A, B and C divide the addresses into a network part and a host part. The difference between the classes is the balance between bits designating network and hosts. Class A addresses have one byte for the network and three for host, B addresses have two bytes for each, and class C addresses have three bytes for the network and one for the host. To differentiate between the classes, start with 0, 1 or 2 bits that are set followed by a zero bit. Class A addresses start with binary "0" and are in the range 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255, class B starts with "10" with a range of 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255, and class C starts with "110" with a range of 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255. Not all addresses are available tor host addresses, however, as some are defined for specific uses (e.g., broadcast addresses). Class D is indicated by "1110" at the start, giving an address range of 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. This class has been reserved for multicast addresses.
When a host wishes to join a multicast group, that is, get packets
with a specific multicast address, the host issues an Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP) request. The multicast router for that subnet will then
inform the other routers so that such packets will get to this subnet and
eventually be placed on the localarea network (LAN) where the host is connected.
Frequently, the local router will poll the hosts on the LAN if they are
still listening to the multicast group. If not, no more such packets will
be placed onto the LAN. When doing multicasting utilizing MBone, the sender
does not know who will receive the packets. The sender just sends to an
address and it is up to the receivers to join that group (i.e., multicast
address). Another style of multicasting is where the sender specifies who
should receive the multicast. This gives more control over the distribution,
but one drawback is that it does not scale well. Having thousands of receivers
is almost impossible to handle this way. This second style of multicasting
has been used in ST-2 [6, 8].
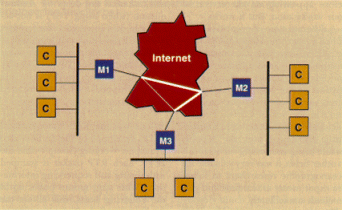
In Figure 1, we have three islands of MBone. Each island consists of a local network connecting a number of client hosts ("C") and one host running mrouted ("M") The mrouted-hosts are linked with point-to-point tunnels. The thick tunnels are the primary feeds with the thin tunnel as a backup.
Basically, a multicast packet will be sent from one client who
puts the packet on the local subnet. The packet will be picked up hy the
mrouted for that subnet. The mrouted will consult its routing tables and
decide onto which tunnels the packet ought to be placed. At the other end
of the tunnel is another mrouted that will receive the multicast packet.
It will also examine its routing tables and decide if the packet should
be forwarded onto any other tunnels. The mrouted will also check if there
is any client on its subnet that has subscribed to that group (multicast
address) and if so, put it onto the subnet to be picked up by the client.
The receiving mrouted will strip off the encapsulation and forward the datagram appropriately. Both these methods are available in the current implementations.
Each tunnel has a metric and a threshold. The metric is used for routing and the threshold to limit the distribution scope for multicast packets.
The metric specifies a routing cost that is used in the Distance Vector Multicasting Routing Protocol (DVMRP). To implement the primary and backup tunnels in Figure 1, the metrics could have been specified as 1 for the thick tunnels and 3 for the thin tunnel. When M1 gets a multicast packet from one of its clients, it will compute the cheapest path to each of the other M's. The tunnel M1-M3 has a cost of 3, whereas the cost via the other tunnels is (1 + 1) 2. Hence, the tunnel M1-M3 is normally not used. However, if any of the other tunnels breaks, the backup M1-M3 will be used. However, since DVMRP is slow on propagating changes in network topology, rapid changes will be a problem.
The threshold is the minimum time-to-live (TTL) that a multicast datagram needs to be forwarded onto a given tunnel. When sent to the network by a client, each multicast packet is assigned a specific TTL. For each mrouted the packets pass, the TTL will be decremented by 1. If a packet's remaining TTL is lower than the threshold of the tunnel that DVMRP wants to send the packet onto, the packet is dropped. With that mechanism we can limit the scope for a multicast transmission.
In the beginning there was no pruning of the multicast
tree. That is, every multicast datagram is sent to every mrouted in MBone
if it passes the threshold limit. The only pruning is done at the leaf
subnets, where the local mrouted will put a datagram onto the local network
only if there is a client host that has joined a particular multicast group/address.
This is called truncated broadcast. As the MBone grew, problems surfaced
which we will discuss later. These problems prompted work on proper pruning
of the multicast tree as well as work on other techniques for multicasting
[1, 5, 9]. Pruning as implemented in the MBone today works roughly like
this: If a mrouted gets a multicast packet for which it has no receiving
clients or tunnels to forward it to, it will drop the packet but also send
a signal upstream that it does not want packets with that address. The
upstream mrouted will notice this and stop sending packets that way. If
the downstream mrouted gets a client that joins that pruned multicast group,
it will signal its upstream neighbours that it wants these packets again.
Regularly the information will be flushed and packets will flow to every
corner of MBone until pushed back again.
From time to time, there have been major overhauls of the topology
as MBone has grown. Usually this has been prompted by an upcoming IETF
meeting. These meetings put a big strain on MBone. The IETF multicast traffic
has been about 100 to 300Kb per second with spikes up to 500Kb per second.
For audio we have vat (visual audio tool) by Steve McCanne and Van Jacobsen of Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory. The nevot (network voice terminal) by Henning Schulzrinne of AT&T/Bell Laboratories is another audio tool.
Video tools are ivs (inria videoconferencing system) by Thierry Thurletti of INRIA in Sophia Antipolis, France and nv (network video) by Ron Frederick of Xerox PARC.
Wb (white board) by McCanne and Jacobsen provides a shared drawing space and is especially useful for presentations over the MBone. Wb can import slides in PostScript and the speaker can make small annotations during the lecture.
Figure 2 depicts the sd (session directory) by McCanne and Jacobsen. Sd offers a convenient way of announcing "sessions" that will take place on the MBone. When creating a session, you specify the multicast address (an unused address is suggested by sd) and the various tools that are used. Other people can then just click "Open" and sd will start all the necessary tools with appropriate parameters.
When this snapshot was taken, the SIGGRAPH conference was taking place. As a special event at that conference, children were invited to talk with people on the MBone. This event is highlighted in the sd snapshot. Going up in the list we have Radio Free Vat. This is the MBone "radio" station where anyone on the MBone can be the "disk jockey." Next up is MBone Audio, which is the common chat channel of the MBone. Everyone is free to join and start a discussion about any subject. Because MBone spans about 16 time zones, Not everyone is at their workstation when you ask "Is there anybody out there?" [7], but there is always someone out there! The Global Mapping Satellite (GMS) sessions are pictures from a satellite above Hawaii. The pictures (composite, infrared or visual spectra) are sent out using imm (Image Multicast Client) by Winston Dang of the University of Hawaii. Second to the top is the Bellcore WindowNet. If you tuned in to this session, you would see the outlook from a window from Bellcore. At the top we have not a session, but a plea. As audio and video consumes a fair amount of bandwidth and MBone is global, rebroadcasting your favourite local radio station onto MBone will put a hard strain on many networks. We will come back to this problem later in this article.
Not shown in this particular snapshot, but a frequent and very popular guest on MBone are the Space Shuttle missions. The NASA select cable channel is broadcast onto the MBone during the flights. The pictures of the astronauts travel a long way and traverse many different technologies before appearing on the screen of your workstation. But it works!

Figure 1. MBone topology - islands, tunnels, mrouted
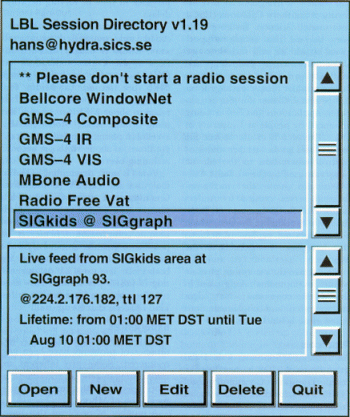
Figure 2. sd - session directory
A different type of event was mentioned earlier, the 1993 JASON Project [4]. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution provided software for Sun and Silicon Graphics workstations so anyone on the MBone could follow three underwater vehicles on their tours in the Sea of Cortez. Position data and some pictures were continuously distributed over the MBone. Beside being interesting for scientists in other fields, it was very valuable for oceanographic researchers to follow the experiments in real time and give feedback immediately.
The multimedia conference control (mmcc) by Eve Schooler of University of Southern California (USC)/ Information Sciences Institute (ISI) goes beyond this simple support given by sd. We will include more about this when discussing the MMUSIC protocol.
The popular Mosaic package from the National Center for Supercomputer Applications (NCSA) is being enhanced by people at University of Oslo. The idea is to use Mosaic for lectures and let the speaker multicast control information to the Mosaic programs used by the students.
We also have the media-on-demand server created by Anders Klemets of Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, Sweden, which offers unicasted replays of sessions that have been multicasted on the MBone.
This is merely a snapshot of some of the developments taking place
in the MBone community. New ideas surface often and implementations follow
close behind.
On top of UDP most MBone applications use the Real-Time Protocol (RTP) developed by the Audio-Video Transport Working Group within the IETF. Each RTP packet is stamped with timing and sequencing information. With appropriate buffering at the receiving hosts, this allows the applications to achieve continuous playback in spite of varying network delays.
Each form ot media can be encoded and compressed in several ways. Audio is usually encoded in PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) at 8KHz with 8-bit resolution giving 64Kb per second bandwidth for audio. Including packet overhead it raises to about 75Kb per second. By using Groupe Special Mobile (GSM), a cellular phone standard, one can get down to about 18Kb per second including overhead.
Video is more demanding. The ivs tool uses the CCITG (Consultative
Committee of International Telephone and Telegraph) standard H.261 [2]
whereas the nv tool uses a unique compression scheme. It is possible to
limit the amount of bandwidth that should be produced in both tools. The
usual bandwidth setting is 128Kb per second. How this translates into quality
depends on the kind of scene that is captured.
A number of problems that have surfaced during operations of MBone
will be discussed in this section. Some problems have a direct bearing
on the MBone implementation, other problems have been discovered recently
during the use of MBone.
MBone in its present form should be viewed as one single resource. Only in a few places can it handle more than one video channel together with audio. The IETF tries to make two video and four audio channels but does not always accomplish this, even if the best "networkers" in the Internet put in their best efforts. So far, we have not had any major collisions of major events. The collisions that have occurred have been resolved after some brief discussions. Essentially it is a first-announce-first-serve scheduling. As MBone increases in popularity, one can expect more collisions and the pressure for a particular slot will increase.
Some of the success of MBone is dependent on the "courtesy" of TCP. When someone starts sending audio onto a fully loaded Internet link, it will cause packet losses for many of the connections that are running on that link. They are usually TCP connections and they will back off when packet losses occur. UDP-based audio does not have any such mechanism and will effectively take the bandwidth it needs.
On several occasions end users have started a video session with a high time-to-live (TTL) and subsequently swamped the network with a continuous stream of 300 to 500Kb per second. These users have not been malicious. Sometimes the program has just been started with "-ttl 116" instead of"-ttl 16" with the effect that it reaches most parts of the MBone instead of just the local part. At other times, the users have not really been aware of what "256Kb per second" really is netwise. Very few links in the Internet can handle that load without severely disturbing normal traffic. Usually after the mistake has been pointed out, the users have stopped their transmissions. The Problem is that with the new video and audio applications the mistakes have severe consequences and with multicasting in MBone, the consequences are spread globally. It will take some time before the user community gets a feel for how much bandwidth video and audio takes. Existing applications like ftp can also use a lot of bandwidth, but the backoff mechanism of TCP ensures a fail split of resources, which a UDP-based application does not.
Lacking a fine-grained resource allocation mechanism, a way to
put a limit on the bandwidth usage of a tunnel could be very helpful. That
would make many network providers a lot less nervous about letting multicast
traffic loose.
The guidelines establish that traffic within one site should be sent with a ttl of 16, within one "community" 32, and global traffic should have 127. The IETF transmission plan is shown in Table 1.
The table says that if you only want get audio channel 1 with the GSM compression, your tunnel should have a threshold of 224.
The threshold mechanism is a very coarse method to limit traffic. With the current IETF plan, there is no way you can use your 256Kb per second link to join the session that is broadcast on channel 1. To get PCM audio 1 you will open up for both GSM audio channels, giving a total of ~105Kb per second. To get Video 1 you will also get the PCM audio 2 summing it up to ~310Kb per second for video and audio from channel 1.
Table 1. Time-to-live (TTL) and thresholds from the Internet
Engineering Task Force
Traffic type TTL ~kb per second thresholdGSM audio 1 255 15 224 GSM audio 2 223 15 192 PCM audio 1 191 75 160 PCM audio 2 159 75 128 Video 1 127 130 96 Video 2 95 130 64 local event audio 63 =>250 32 local event video 31 =>250 1 When true pruning gets widely deployed in MBone it will be possible to get only what you ask for.
A related problem is saturation of the local Ethernets. FIX-West
had 15 tunnels during the IETF meeting in March 1994. With an IETF load
of ~500Kb per second it results in ~6.5Mb per second pushed over the FIX-West
Ethernet. Even without the MBone traffic, that Ethernet is already busy.
Some mrouted operators use the cpu overload as a means to limit the impact
on the local network. That is, if you have a SPARC 1+ as a mrouted host,
it will not push more than 1,000 packets onto the net, probably much less.
This is a dangerous practice unless you are the only entry point to a part
of MBone. As stated previously, when your tunnel gets declared dead, MBone
will choose another route if possible until your mrouted gets its breath
back. This results in heavy route flapping, which becomes a global problem.
If you are the only path to take, traffic will just stop for a while, which
is a local problem only.
During the packet video workshop at MCNC, Van Jacobson observed a phenomenon in which it seemed that routing updates severely impacted the audio transmissions. The congestive loss rate was about 0.5% but every 30 seconds he observed huge losses (50% to 85%) for about 3 seconds. Jacobson concluded that it was due to the LSRR option processing competing with routing updates. Not only does this affect MBone traffic, but also other traffic such as pings and traceroutes.
Many hosts and routers do not handle multicast traffic properly.
Often they respond by sending an ICMP redirect or network unreachable.
These responses are not in accordance with the IP specifications. This
is usually not a problem until we have several such hosts reacting with
ICMPs to a number of audio streams of about 50 packets per second. The
any network tends to get flooded with ICMPs. It has happened that a site
was disconnected from MBone due to a "screaming" router. Over time, this
problem has diminished as router vendors update their software. Also, with
the new encapsulation tunnels, the ICMPs will be sent to the last tunnel
endpoint, not the entire route back to the original sender.
Some of these issues are still difficult research issues, like resource control and real-time traffic control. Other work is directed toward better management hooks and tools and incorporating multicasting in the Internet routers. Maybe there are better technologies for multicasting than those currently used in the MBone? The IDMR (Inter-Domain Multicast Routing) working group in IETF is working on this.
MBone has enabled a lot of applications. One problem when starting the applications is the question of what addresses should be used. Picking one randomly will be fine for quite a while, but eventually when MBone gets more crowded some mechanism has to be put in place for allocation of multicast addresses and port numbers.
As MBone is today, the sender has no control or implicit knowledge of who is listening out there. A receiver can just "tune in," like a radio. Some applications would want some kind of information about who is listening, for example by asking MBone which hosts are currently in a particular multicast group. There are mechanisms in some applications for end-to-end control of who is listening (i.e., encryption) but there is so far no common architecture for this. When the going gets rough and a lot of packets are dropped, some applications would be helped by some feedback on the actual performance of the network. A video application could for example, stop sending raw HDTV data when only 2% make it to the receivers and instead start sending slow-scan, heavily compessed pictures.
We look forward to the next round of developments as the MBone
continues to evolve.