The operating system consists of software that is designed to exercise the hardware-defined interface and, usually, to make it easier to use and less specific to the interface of a particular machine or model of machine. Thus the operating system is usually organized into two or more layers. The "bottom" layer interfaces to a a specific machine. Each layer above the bottom adds a set of abstractions that hide some of the detail of the layer or layers below. In so doing, each layer
In the case of Linux (which is a derivative of Unix), the goal has been to minimize the hardware specific "bottom" layer to make it "easy" to port Linux to new hardware. Originally, the hardware specific code was contained in a single assembly language file that contained approximately 2000 lines of assembly. In theory, only that one file needed to be specialized for a new machine to run Unix/Linux.
Today, the machines that are available are significantly more complicated so the porting effort is non-trivial. However, once the low-level routines are ported, the Linux kernel (which consists of many layers) will run.
In this software architecture, there is one OS "bottom" layer that supports the OS on a given machine. The OS may support multiple users (using OS processes to isolate each user's access from the others) but is in THE OS that ultimately controls the hardware directly.
At some point in the mid 1990s it became clear that the OS had become much more an extension of the applications that it runs than an interface to the hardware. Operating systems such as Windows had begun to "push" application functionality into the operating system (e.g. Internet Explorer became partially embedded in Windows). Similarly, Linux and FreeBSD (the basis for Apple's OSX) began to include more and more functionality in the OS abstraction layers to support their applications (e.g. Apple's Cocoa).
In short, to run an application (like Microsoft Word) required that the machine run the OS that supports the application. That has been more or less true for some time, but the complexity of the operating systems combined with the degree to which they embedded application-specific functionality made cross OS support more and more difficult.
The "solution" was to interpose a software layer between the "bottom" layer of the OS stack and the hardware that was capable of supporting multiple "bottom" layers simultaneously. Operating System Virtualization refers to the notion that an OS can be made to execute on a set of software abstractions rather than on the hardware itself.
Note that under this definition it is possible to question whether "containers" are a legitimate approach to OS virtualization. We'll address that question in the section on containers but the question can certainly be argued either way. Containers are able to provide similar high-level functionality as long as the operating systems that are sharing the hardware are the same or compatible with the same set of OS abstractions. They essentially choose a much higher "bottom" layer to lift off. We'll discuss containers more at the end of these notes.
Virtualization, like many terms associated with cloud computing, is often ill defined. For the purposes of this course (and as a good benchmark definition) virtualization is
the process of abstracting the physical machine hardware to the point where it is possible to run a full operating system using the abstractions only.
That is, a virtualized system is one in which the operating system "thinks" it is running "alone" on a physical machine, but instead it is controlling abstractions in place of the physical hardware.
Even this definition is a bit tricky since Intel introduced hardware support for virtualization. These extensions to the x86 architecture implement in hardware "abstract" versions of other hardware features (like page tables) calling into question the definition of the word "abstraction." From a processor architecture perspective, then, virtualization is the isolation of physical machine resources such that a full machine operating system can use the resources independently as if they machine were dedicated to it.
From a systems design perspective, virtualization is the notion that the operating system (and not the process) is the resource container that provides isolation. That is, each operating system believes it has full control over a set of machine resources and some other "system" (usually called a hypervisor) is able to arbitrate sharing among operating systems (in a way analogous to the way in which an operating system arbitrates sharing among processes). The Linux containers community might take exception to this last definition but so be it.
Virtualization (as it is commonly implemented today) attempts to meet two requirements:
There are generally four approaches to virtualization:
Today, the most widely used datacenter virtualization technologies are VMware, KVM, and Xen. However the developer community has embraced the packaging features of Docker (which depends on a Linux container) to such an extent that containers have become an important component of many software delivery mechanisms.
In an unvirtualized setting, the job of implementing isolation falls to the operating system and the unit of isolation is the process. That is, each user can launch one or more processes that she "owns." Within each process, the user appears to control all resources (memory, cpu, network connections, etc.). Outside the process, however, the operating system implements mechanisms that allow multiple processes to share the resources (memory, cpu, network, etc.) of a single machine. This sharing is a form of isolation because the actions a program takes within a process do not need to take into account the existence of other processes. For example, the cpu registers that implement the memory stack appear dedicated to the process and, as a result, the program does not need to guard itself against another user's use of the stack.
Process isolation simplifies program development and, in some cases, improves software engineering (by isolating software faults).
Modern hardware provides support for process isolation using two built-in facilities: memory protection (typically via virtual memory) and system calls. Memory protection allows the operating system to dedicate a portion of the physical memory to a process and (most importantly) to reclaim that memory from the process when the operating system need to give it to another process. System calls allow a process to transition control flow into code that is trusted to control the hardware directly according to the isolation specifications. Thus a process executes code in a protected memory region. When that code needs to manipulate shared hardware resources in a way that might allow it to violate the isolation properties of the operating system, it makes a system call to trusted code that first checks the access and performs it only if it is within specification (e.g. the process is accessing disk sectors according to the permissions scheme implemented by the OS).
To implement OS virtualization, the system must have access to analogous functionality. It must be able to provide memory protection between virtualized operating systems (that are otherwise given autonomous control over their memories) and it must provide a method of transitioning control flow into trusted code when an OS wishes to perform an operation that could possibly violate isolation.
In general, a virtualization methodology must
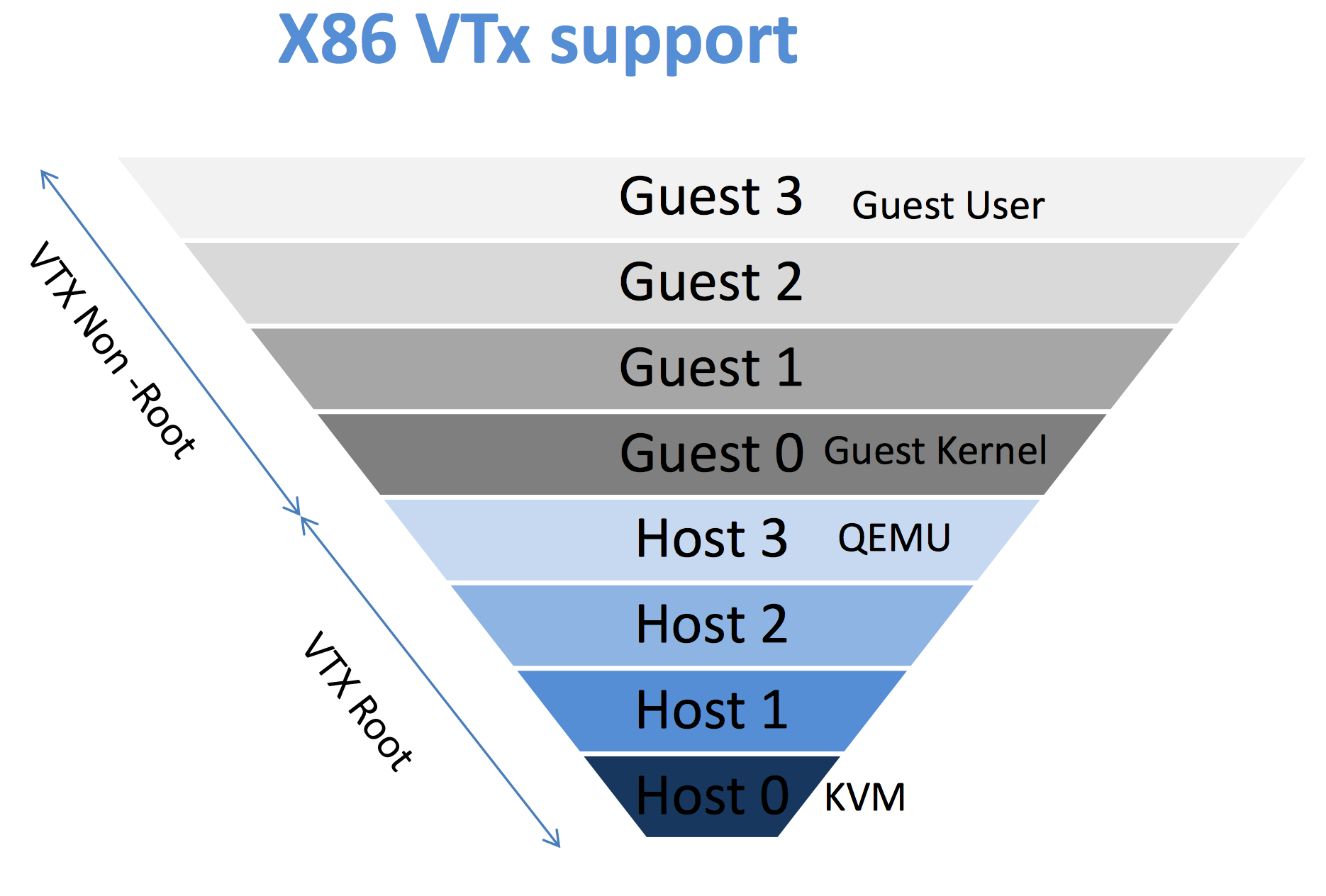
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is an open source virtualization technology currently supported by the Linux kernel for the x86 architecture. It is based on an earlier (and more portable) system called QEMU (see another wonderful tutorial by Steven Hajnoczi) that uses a software emulation which (while portable) carries a significant performance penalty. KVM relies on virtualization hardware facilities that are now available for many (but not all) of the Intel processors that are compatible with the x86 instruction set architecture. Intel terms these capabilities "Intel VT" and they come in the form of "VT-x" and "EPT." The community typically refers to these as "HVT" or "HVM" for "hardware virtualization technology" or "hardware virtual machine" support.
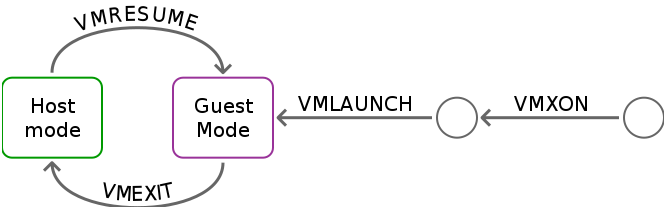
KVM uses VT-x to implement protected state transitions between a guest and the hypervisor. With VT-x, the processor defines two new protection modes: host mode and guest mode.
Thus Intel added host mode and guest mode. In each mode, the processor can be set in any ring. However protected instructions from Guest-0 generate faults that can be checked in host mode.

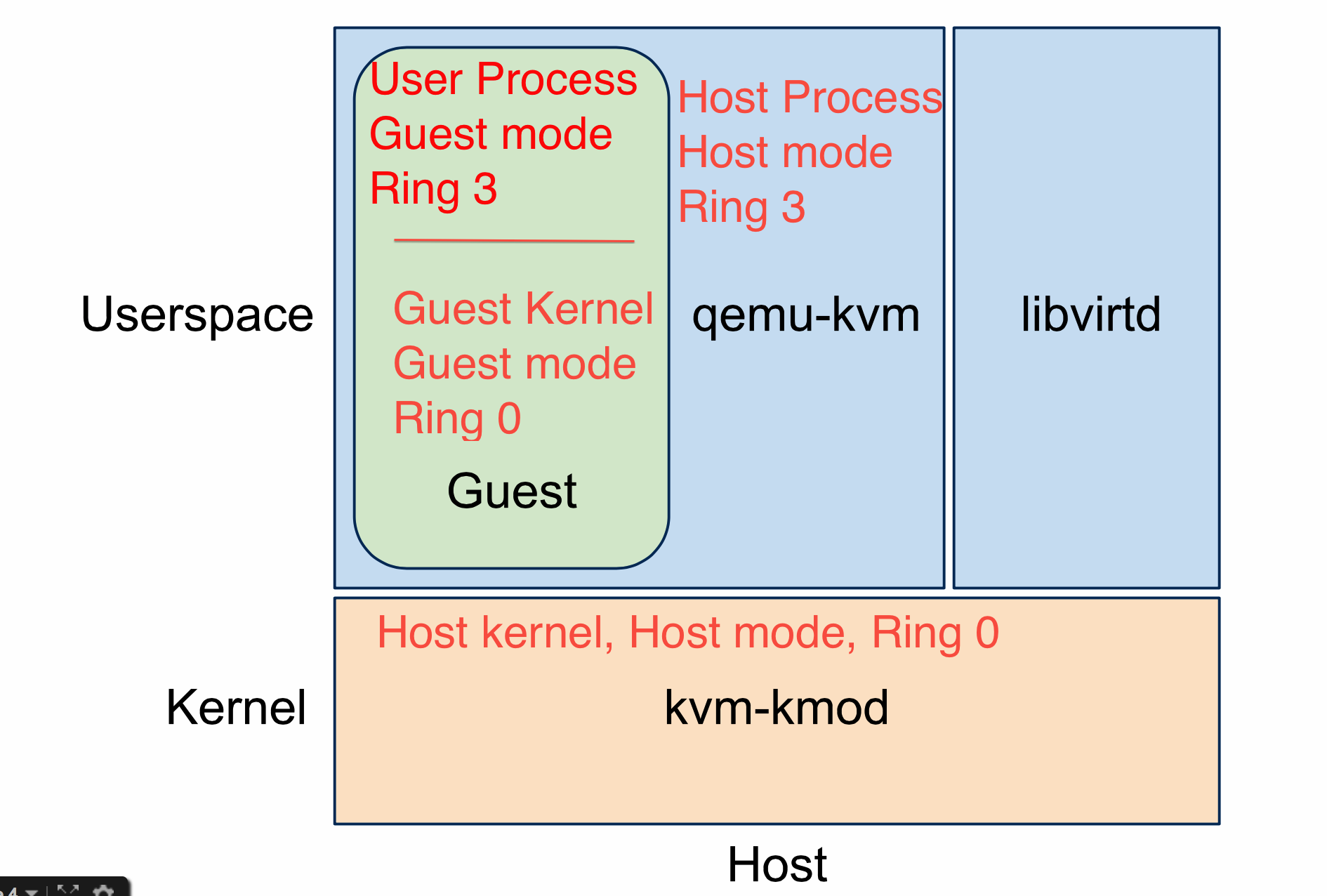
The main idea behind KVM is to run a process on the host OS that KVM turns into a guest OS. To do so, a host OS process loads up the code for the guest that is necessary and then "launches" the VM in the correct guest mode ring level. Using the hardware triggers provided by VT-x, KVM (host ring 0) directs privileged events to QEMU code (running in host ring 3). If you are stuck with the Linux process model in your head, then the way to think of this is
The state management via VT-x is relatively straight forward in that the extensions define a data structure to consult (set up in Host mode) when making transitions.
When the guest requires service when either
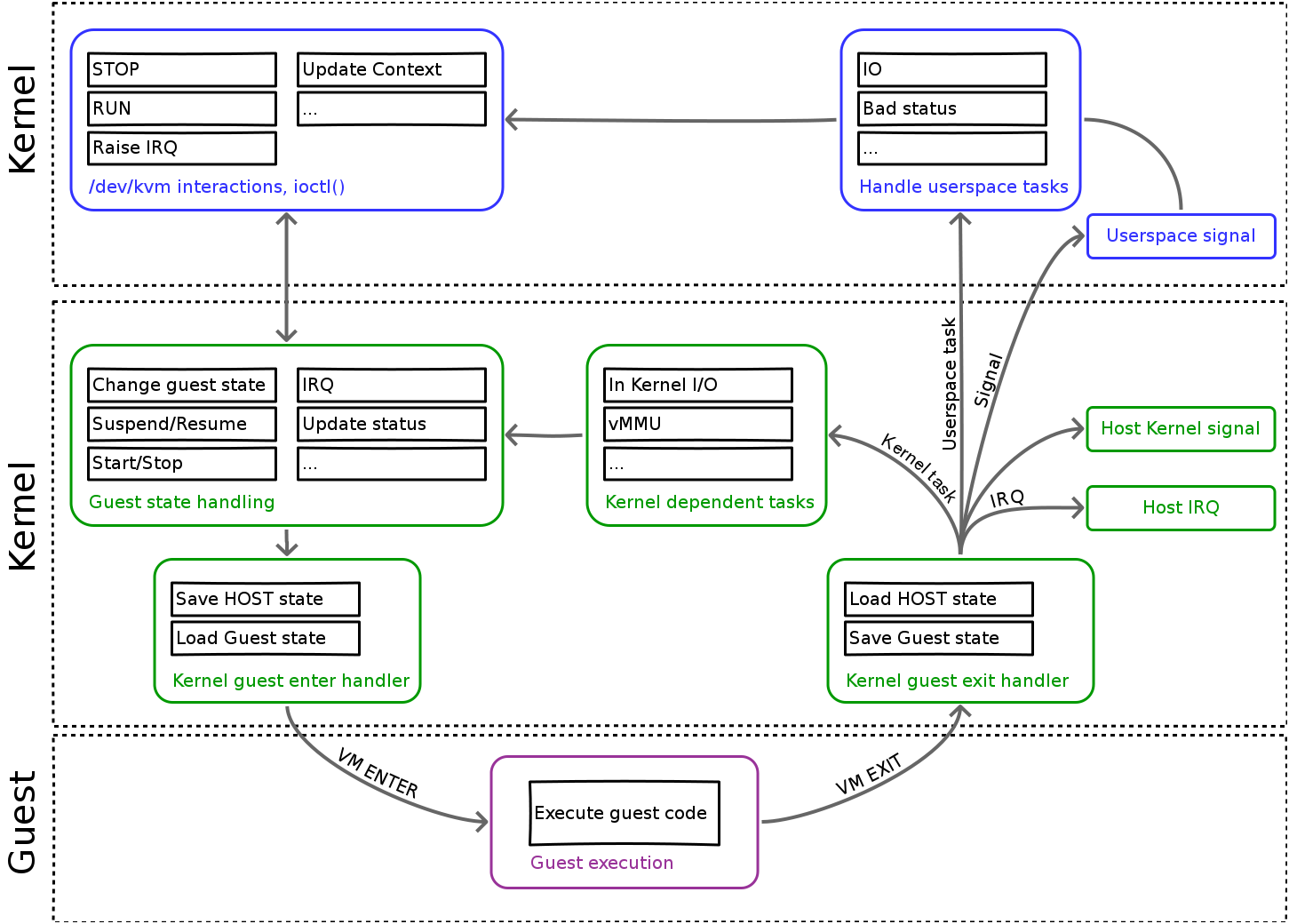
In the case of hypervisor functionality, unless it is a simple kernel function, KVM pushes the actual processing into a user space process (QEMU) by returning from a system call that the process has made that has been blocked. When QEMU handles the request, it calls back into the host kernel via the system call.
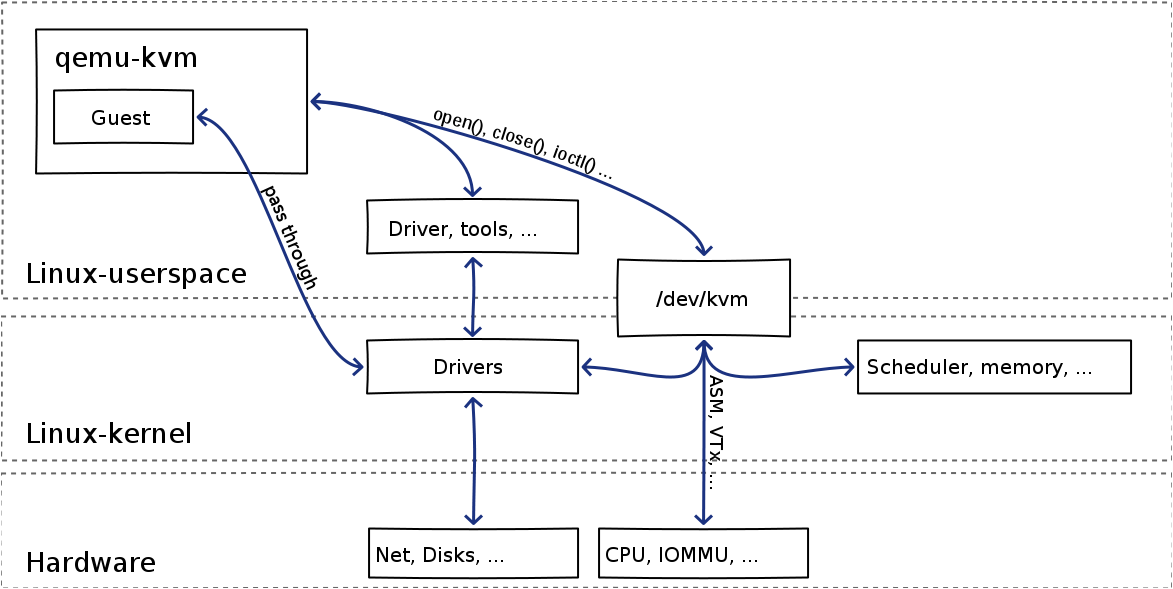
This previous discussion outlines the control flow relationships between a guest process, a guest kernel, KVM, the host kernel, and a host process (that contains the guest process, the guest kernel, and the QEMU code). Notice that the goal of KVM is to make a guest OS "look" like a regular process to the host OS since most of the functionality needed to service the guest is actually available in the host. Notice also that the guest doesn't "know" it is embedded in a host process because the VT-x support handles transitions into the hypervisor when ever the guest might be doing something that requires privileged control.
This high-level description is intended to cover control flow transitions. Notice that in an operating system, control flow can take many forms, almost all of which are asynchronous from the perspective the operation system kernel (guest of host). For example, when the hardware timer interrupts, it throws an interrupt to the host kernel. That interrupt may also need to be vectored (dispatched) to a guest kernel that need to keep track of the time as well. KVM in the host is responsible for handling interrupt dispatch. It uses the VT-x extensions to transition between host mode (where the interrupt is initially fielded) and guest mode (where the guest kernel's interrupt handler must be executed). When KVM initializes a kernel, part of the boot-up process is to record how interrupt dispatch is to be implemented for the guest.
In addition to governance, the memory system also implements efficient resource utilization in the form of demand paging. When a legal page from a process is needed and is not already present, the process throws a page fault that the kernel catches and services.
The key data structure for implementing process memory management is the page table. The page table format for the x86 is defined (it is a two-level hierarchy) by the architecture. Thus, each legal page of process memory is described by two page table entries -- a page directory entry (top level) and a page table entry -- that are check on every memory access.
To make this checking fast, each processor version also includes a TLB that caches recently used page directory and page table entries. The implementation of the TLB varies but it in each case it is designed to short-cut a full page table lookup if the mapping information has recently been accessed.
Herein lies the rub.
The x86 architecture is designed with the notion that there is one page table and one TLB per operating system. Worse, each page table entry refers to a physical frame number in the machine's memory. Thus each guest will believe that it has the ability to use all frames in the physical memory -- a situation that the hypervisor must prevent.
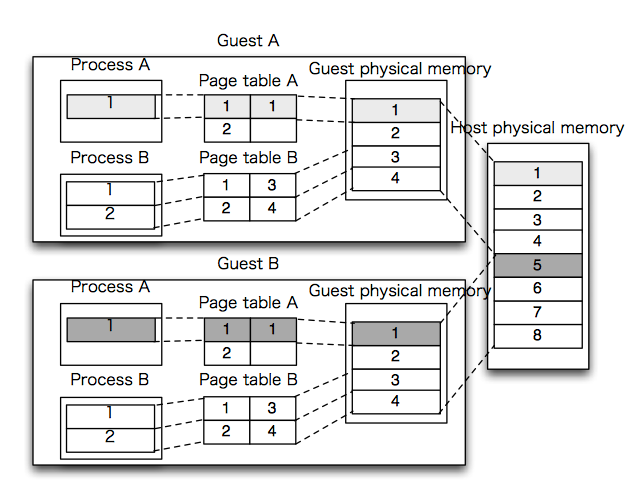
In the case of KVM-style virtualization, however, each guest has a page table as does the host. Further (unlike in the control-flow case) it is not possible to interpose KVM on each memory access because the access checking is done strictly in hardware.
KVM relies on another Intel VT feature called the "Extended Page Table" (EPT) to resolve this difficulty. EPT allows the host kernel to set up a "shadow" page table in the processor that gets used when the processor is running in guest mode. It is a shadow page table in that it gets used by the hardware to check memory accesses (like a true page table). However, the references in the shadow page table are to host page table entries (the host page table essentially forms another two levels of hierarchy). Thus, the host can maintain one, large page table that it partitions among guest page tables, each of which "believes" it has the full, unshared memory space.
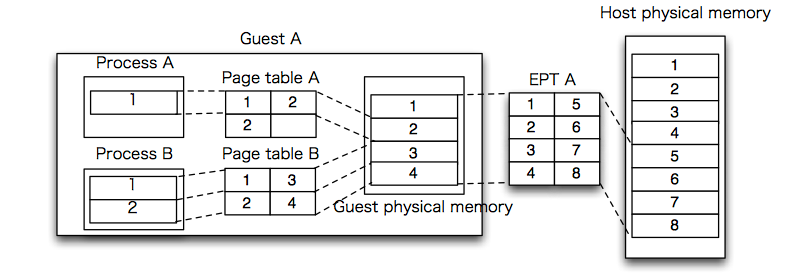
TLB management in the case of EPT is a joy, to put it mildly. Notice that "the" TLB for the machine now needs to handle shadow mapping and host mapping. Worse, when a guest VM is descheduled because another guest is to be run, the TLB entries for the old guest must be invalidated. In an unvirtualized setting, the TLB is usually flushed at process context switch time for the same reason. However, with an extra level of indirection, a full flush can cause a serious performance problem. Thus EPT (in some implementations) also implements a tagged TLB which allows the hypervisor to decide on exactly which TLB entries to flush when guests are switched.
The careful reader at this point may be troubled by the lack of a discussion of I/O in KVM. This omission is intentional and for the sake of brevity rather than due to negligence or maliciousness. KVM's original I/O model was designed to support "full" virtualization in the sense that the guest OS did not need to cooperate. To implement full virtualization, the I/O devices had to be emulated at a very low level so that guests would be able to use their own native device drivers without modification. Thus the original KVM contained software emulations of hardware Ethernet cards and SCSI disk controllers that "pretended" to be physical hardware devices. While flexible, this approach suffered from I/O performance penalties that led the KVM community to move away from full virtualization for I/O. Virtio is an effort to use paravirtualization (described below in the context of Xen) for I/O as a way of alleviating this performance issue. The non-paravirtualized KVM I/O features are still available, but the rumor is that they are being phased out as support for Virtio makes it into other operating systems (like Windows).
Virtualization is generally thought of an an IBM invention from the early 1970s. More recently (mid 1990s), VMware implemented virtualization for the x86 hardware using several different techniques (the industrial versions of which being similar to KVM's approach). However, the first technology to make virtualization available as open source at a large scale was Xen. Like VMware and KVM, Xen's technological goals for virtualization were to implement isolation at a level of abstraction that could permit operating systems to function independently of each other and of their host.
However, the Xen approach differed from VMware and KVM (QEMU) in a few important ways. First, Xen was concerned, primarily, with the performance of virtualized operating systems. At this time it was founded, hardware support for virtualization was not widely available meaning that some form of software emulation was needed. VMware used (among other techniques) binary rewriting of guest OS code to insert emulation and QEMU was simply a full emulation system (although it also adopted binary rewriting in very clever ways). These techniques permitted full virtualization but there was concern within "the community" that they were too slow to be of practical use on an industrial scale.
To meet the performance challenges as they saw them, the Xen team decided to sacrifice the notion that a virtualized guest could be hosted without modification. That is, Xen decided not to implement full virtualization but, instead, to implement paravirtualization which relies on changes to the guest. The key idea centered on changing the way in which each guest OS interacted with the x86 protection mechanisms so that isolation could be implemented without additional hardware extensions.
The basic concepts behind Xen are deceptively simple. The goal was to run the guest in ring 1 of the x86 protection hierarchy. As with KVM, Xen had to solve the problems of
Unsurprisingly, the Xen architecture is also different than KVM's
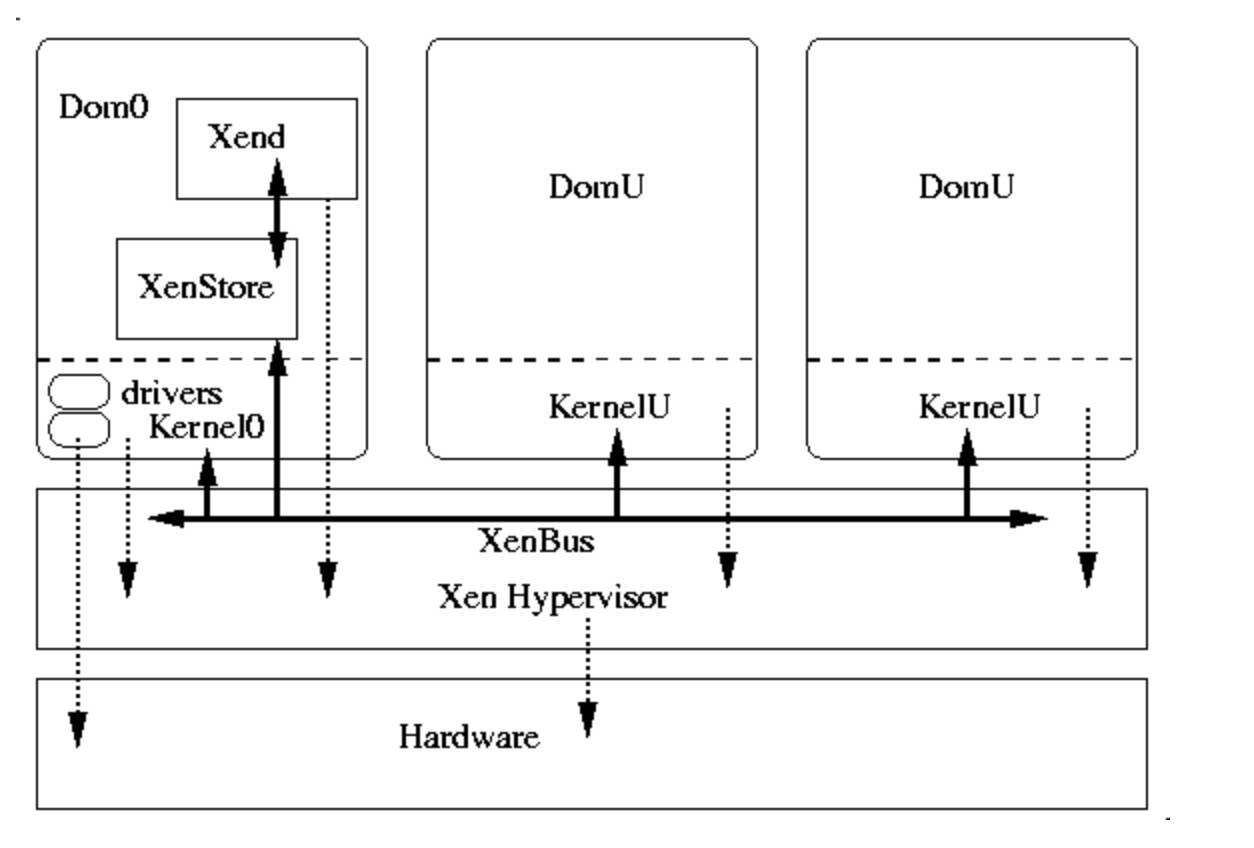
The guest is not logically a process from the perspective of the host. Rather, each guest runs independently on the hypervisor which (in theory) is the control software for the host. That is, there is no host OS running in ring 0. Instead, the hypervisor runs in ring 0, and each guest runs in ring 1.
If implemented completely literally, this architecture would require the hypervisor to include device drivers and user-interface code to allow guests to access hardware resources and to control the system. To avoid this complexity, Xen allows for a "special" guest to be specified (called "dom0" -- pronounced "dom zero") that also runs on the hypervisor. Guests, in the Xen parlance, are each termed "domU" to indicate that they are each a user "domain."
Under Xen, dom0 serves two purposes:
To implement privileged control flow, each guest must be examined and modified so that each ring 0 instruction that cannot run in ring 1 be translated into a trap to the Xen hypervisor. The binary rewriting techniques discussed briefly in the previous section perform the same function, but at the instruction level without changes to the guest source code.
Xen's approach was to mandate that all such changes be made at the source level in the guest and that the guest be recompiled for execution with a Xen hypervisor. Working at the source level is, in some sense, easier since the operating system source explicitly encodes its privileged operations. Further, well modularized operating systems typically group these privileged operations together into a common set of modules, both to promote portability (these are typically architecture specific) and robustness (they are shared among all OS subsystems).
One often overlooked issue with this approach is that it also changes the failure modes of the guest. In a full virtualization setting, the guest either runs or it appears to the guest that the hardware has failed. Under Xen, a guest may have misimplemented its Xen-specific code but otherwise be intact. Xen needs to ensure that any misimplementation in the guest does not compromise the overall system and also that the guest fail gracefully due to such a misimplementation.
All privileged instructions that must be implemented securely in ring 0 must be replaced in the guest with a special kind of system call termed a hyper call. Like a system call, a hyper call pushes arguments on the stack (or marshals them in registers for speed) and then issues a "trap" instruction that causes the processor to switch to ring 0 and to jump to a well-known (and trusted) location so that the hyper call can be serviced. That is, a hyper call is really just a system call that a guest OS makes from ring 1 to ring 0 in (more or less) the same way that a guest process makes a system call from ring 3 to the guest OS in ring 1.
Notice that traps themselves may need to be changed and also that interrupts must be vectored by the hypervisor in the same way as they are under KVM. However, because the guest can be changed, rather than intercepting them, Xen implements an event system that guests use to ask the hypervisor for interrupt support. Thus, interrupt code in the guest falls under the broad rubric of "privileged" code that must be modified. We'll discuss this issue further in the section on paravirtualized I/O.
Thus Xen mandates that the guest change all of the code that attempts to write data into a page table entry (page directory or page table) to make a hyper call instead. It enforces this restriction by making the memory used to implement the page tables read only. Thus an attempt by a guest to write its page tables directly will cause a fault (which the hypervisor catches).
The other part of Xen cleverness with respect to memory management has to do with how it manages the virtual to physical mapping of memory. With HVM, Xen supports shadow page tables (in two different ways). Without HVM, however, it allows each guest to "see" the physical frames in memory it has been allocated. When a guest needs a physical frame, it requests one from Xen and Xen expects that the guest will keep its own mapping of how that frame is used.
One way in which the frame is used is in a page table entry. When a guest creates a virtual to physical mapping in a page table entry (as noted above) it must request that Xen update the page table on its behalf. Xen checks to make sure that the physical frame number specified in each update is "legal" for that guest (i.e. that the guest owns the physical frame).
This technique will work in any situation where the guest must use a physical memory address as long as the guest requests state updates from Xen. For example, a guest that wishes to initiate a DMA will supply a physical frame number, but Xen must be able to check that the guest owns the frame before sending the DMA request to the machine's DMA controller.
The approach is called The Split Driver model. Each device is controlled by two drivers (one used by the guest and one used by dom0) that work together. The model is essentially an RPC-like model in which a client operates an interface that marshals arguments and communicates them in a canonical transport format to a server that unmarshals them and executes any commands that are contained therein. Results from the execution are marshaled and communicated back to the client where they are unmarshaled and presented to the user.
In Xen, the guest driver (called "the front end") is analogous to the client in an RPC setting. It is responsible for implementing the driver's interface to the guest and for communicating device requests to the "back end" of the driver running in dom0. The back end operates the specific device and returns what ever results are needed by the front end to communicate to the guest.
The communication mechanism between front end and back end is a combination of shared memory, queuing, and asynchronous events. Xen includes a facility (called Grant Tables) that allows access controlled sharing of pages between domains (all domUs and dom0). Thus one domain can send a page to another by allowing it to be unmapped in the sender and mapped in the receiver without the overhead associated with copying the data. Xen split drivers use this technique to send data between the front end and back end and vice versa.
Each data transfer is associated either with a request event or a response event. Further, most (but not all) devices implement essentially a write/read model of I/O (from the perspective of the guest). Thus the guest initiates an I/O by writing a request from the front end to the back end. The back end reads these requests, services them with respect to the device, and writes a response that the front end later reads.
Requests and responses are managed in a ring that logically lives in Xen's memory. The ring only contains event descriptors (the data is moved separately using shared pages if possible). In addition, both the front end and back end portions of the driver can register a call back for Xen to run when a descriptor requires processing.
It is through this event delivery mechanism that Xen achieves I/O virtualization. Events are delivered over "channels" that are set up in the hypervisor so that each guest appears to have exclusive access to the devices configured in the system. The event mechanism ensures that requests from one guest are not delivered to another nor is it possible for one guest to pretend to be another. The front end of the driver must also be modified to trigger any necessary interrupts in the guest in response to event delivery.
Like with KVM, this high level description does not portray the complexities associated with the implementation of these concepts. The x86 architecture is really several architectures (some legacy) all of which must appear to function properly when executing a virtualized guest. The details associated with this proper function are, to be sure, non trivial.
Then, for reasons that are somewhat obscure, the two main Linux distros (Fedora/Red Hat and Ubuntu) dropped Xen support in favor of KVM. There is some debate among The Clouderati on the importance of Linux distros in the time of cloud. The shift in popularity from Xen to KVM was, in part, driven by the decision to drop support in just two of the distros, which is a fact worth considering.
Currently, it seems that Xen is back in Fedora 16 and Ubuntu (at least, at some level).
From a performance perspective, the direct paging scheme described above (paravirtualized memory without HVM) was considered too slow for many Linux functions (like fork) that required large numbers of page table updates. Xen's HVM support is faster, but (like KVM) it really depends on having a good TLB hit rate to get close to native speed.
Contrary to popular belief, paravirtualized I/O seems to be best practice for open source Linux device drivers. Much of the resistance to paravirtualization was centered on the perceived inability to use it for proprietary operating systems like Windows (because they are not open source). Windows support for Virtio is now available, however, so that impediment seems to have been specious.
There is another way to look at the problem of isolation, however, and that is from the perspective of the user and/or the process. A user of a virtualized operating system is, fundamentally, running a process. It is possible to consider a virtualization approach that isolates a process rather than the operating system in which the process is running.
This approach is the one that is implemented by Linux containers. There have been other container approaches (Parallels is perhaps the best known) but LXC is the current leading technology with respect to the main line Linux kernel and distros.
The main idea behind Linux Containers in general, and LXC in particular, centers on the notion that processes can be made to implement user isolation in a way that provides a similar degree of user control that OS virtualization does. Specifically, one of the advantages of OS virtualization is that it allows each user to run as root in her own OS. At worst, a user can damage her own OS instance by misapplying root privileges but such effects are restricted to the instance by the hypervisor.
If the user could be given root, she could manage her process tree as if she were "the root" in an OS if her actions as root are isolated.
Thus the goal of Linux containers is to implement an isolation mechanism that is comparable to OS virtualization using the Linux process abstraction.
LXC is an amalgamation of several Linux features including
Moreover, the kernel maps can ensure that different processes use the same name for separate machine resources, thereby implementing isolation.
For example, namespaces allow a process to change the the Linux hostname that it (and all other subprocesses) get back from a call to gethostname() without changing the host name that other processes get. Without namespaces, the kernel keeps a record of the hostname for the host. A call by root to change the host name changes it for the entire system and all calls to get the host name return what ever the current value is.
With name spaces, a process (as root) can change the host name and only it and its descendants will see the change. All other processes are unaffected.
Linux currently implements namespaces for six types of resources:
However, with namespaces in place, it is possible to create a process (say when a user logs in) that has a complete set of Linux "names" allocated to it that can be changed from within the process (thereby affecting all children) without affecting other processes. In particular, using chroot, it is possible to make the file system that the process sees as the root file system look like the root file system of an unvirtualized Linux system. The boot code and logic won't be affected, but all other Linux functions can then execute within the namespace as if they are running on a non-isolated kernel.
LXC does all of the housekeeping (and there is a great deal of it) necessary to create a namespace that can run a full Linux distro as if the distro were running alone on a Linux kernel by itself.
The problem here is that the Linux kernel inherits from Unix exactly the opposite design specification from that which LXC is attempting to implement. That is, the original designers of Unix were trying to remove the possibility of isolation from the OS in their design (as a way of promoting sharing). LXC is, in some sense, attempting to retrofit isolation into a system explicitly designed not to support it.
Namespaces are an elegant solution for logical isolation, but because the kernel is shared, the processes can still interfere with each other because they are still sharing the same set of kernel resources. Further, Linux contains only modest kernel level features that are designed to prevent the activity of one process from affecting the performance that another gets from the system. For example, memory intensive jobs that cause the system to page to the disk frequently affect system responsiveness for all jobs. Linux does its best to try and be "fair" about system usage, but the fundamental model used by the original Unix authors is that all processes on the system are assumed to belong to a group of users that are cooperating. Thus performance isolation is not an original design feature.
Linux cgroups attempt to add the concept of performance isolation to the kernel in a way that permits fine-grained control. There are 11 different subsystems that can be controlled separately via an extensive set of configuration files. These files -- together -- constitute a policy specification for the cgroup that governs all processes assigned to the group. A running process can be added to at most one cgroup and it and its children will be controlled by the policies specified therein.
LXC combines namespaces and cgroups so that isolated processes will get controlled fair use of the kernel resources. That is, each separate namespace will be entitled to use a specific "fraction" of the kernel resources that are available thus partitioning the Linux machine into separate isolated Linux instances.
First, it is important to understand whether a comparison should be made with respect to the intersection of capabilities or not. That is, one can ask
Given the subset of functionality that is common to all alternative approaches, which is best?
When one encounters the debate between OS virtualization proponents and Containers proponents, this is usually the form of the question that is assumed tacitly. Even then, however, the debate is not as straight forward as it might seem.
Containers are an excellent choice (perhaps the best) if the goal is to provide hosted Linux access. That is, if the goal is to provide a facility where users can provision their own Linux systems and they don't have strong preferences for the specific Linux they need, containers work well. In particular, they can achieve much higher tenancy densities that virtual machines yielding better server consolidation.
However, the use cases for which this advantage is obvious is much more narrow than one might believe initially. For example, if the Linux usage is to host web services, the networking model that LXC implements is troublesome in that it doesn't really allow "standard" networking configuration techniques to work. Put another way, containers are virtualized Linux access -- not virtualized Linux infrastructure. If the applications running under Linux require infrastructure support, the containers are not necessarily better.
Another difference is with the ability to host a variety of different operating systems. Obviously, LXC can host Linux guests and not Windows, for example, Less obviously, different Linux distros can also be problematic due to kernel affinity. That is, each disto version is developed against a specific version of the kernel. Often, to run a version one must change the kernel to match the version compatible with the distro. All hosted Linux on a container system must share the same kernel. Thus, the container Linux can only host distro versions that are compatible with its kernel. Worse, when the container machine upgrades, it can change the distros that can be supported.
Thus, in a cloud context, determining which is "better" is a difficult task. For IaaS, clearly OS virtualization has become predominant. However, as PaaS evolves (where applications have less contact with the infrastructure components Linux exposes) containers may prove to be a better choice. It isn't yet clear.
However Docker is not properly a virtualization approach. Rather it is an easy-to-use technology for initializing and configuring a Linux Container. Originally, Docker depended on LXC but as it evolved it began to use the constituent LXC components directly through their respective Linux interfaces. Docker performs two functions
Thus, Docker is a convenient and powerful way to package software that can then be automatically instantiated as a running program in a container. Because the dependency management and the container runtime are so tightly coupled in Docker, users often do not differentiate between the two.
You might ask "Why not create a dependency management system for virtual machines?" There are several such systems (Ansible, Puppet, Salt Stack, Terraform) but a key difference is that they assume that a virtual machine will be executing in some datacenter or cloud -- Docker does not. That is, Docker fundamentally assumes that you are creating a single, stand-alone application component that will run in a container. The cloud scripting systems are more general (and thus more complex and error prone to use) because they assume that the software must execute on infrastructure as part of some software ensemble.
What follows is due to a really great introduction by Justin Ellingwood.
Kubernetes (K8) provides runtime services (and not packaging services) for distributed containerized applications. Each of its services implements a set of abstractions that can roughly be categorized as follows.
At first glance, it might seem like K8 reinvents IaaS. Current IaaS offerings include the ability to define clusters (using virtualized networking), the ability to control replication (e.g. AWS autoscaling groups), support for workflows, load balancers, etc. Why is K8 not just IaaS by a different name?
Probably the best way to think of it is that K8 specializes and abstracts IaaS so that it can be deployed across IaaS vendors and on native hardware. For example, a K8 cluster is a very specific way to configure a cluster -- with a single head node and relatively unsophisticated worker nodes. This configuration is supportable on on just about every IaaS platform and (most likely) on bare metal infrastructure. However IaaS services are capable of supporting more sophisticated virtualized cluster configurations as well).
Pods define sets of containers that must be assigned to the same node within a cluster. These containers communicate via a shared file system but they logically form a single application component. Again, it is possible to implement this abstraction on just about any IaaS service because it is a special case of a more general assignment policy.
Perhaps the most useful abstraction is the Service abstraction. Linux Containers are difficult to connect to a network. Because devices are not virtualized, there is no way to multiplex a network controller among containers. Instead, each container must route traffic through a virtualized gateway. Configuring this gateway is tedious and error prone but is absolutely essential if a containerized application is to be reachable over the network. Thus, a big argument for the use of K8 is that is drastically simplifies the process of creating a network facing application from one or more containerized software components.